I Am Sober is a free app that helps you get some control back in your life.
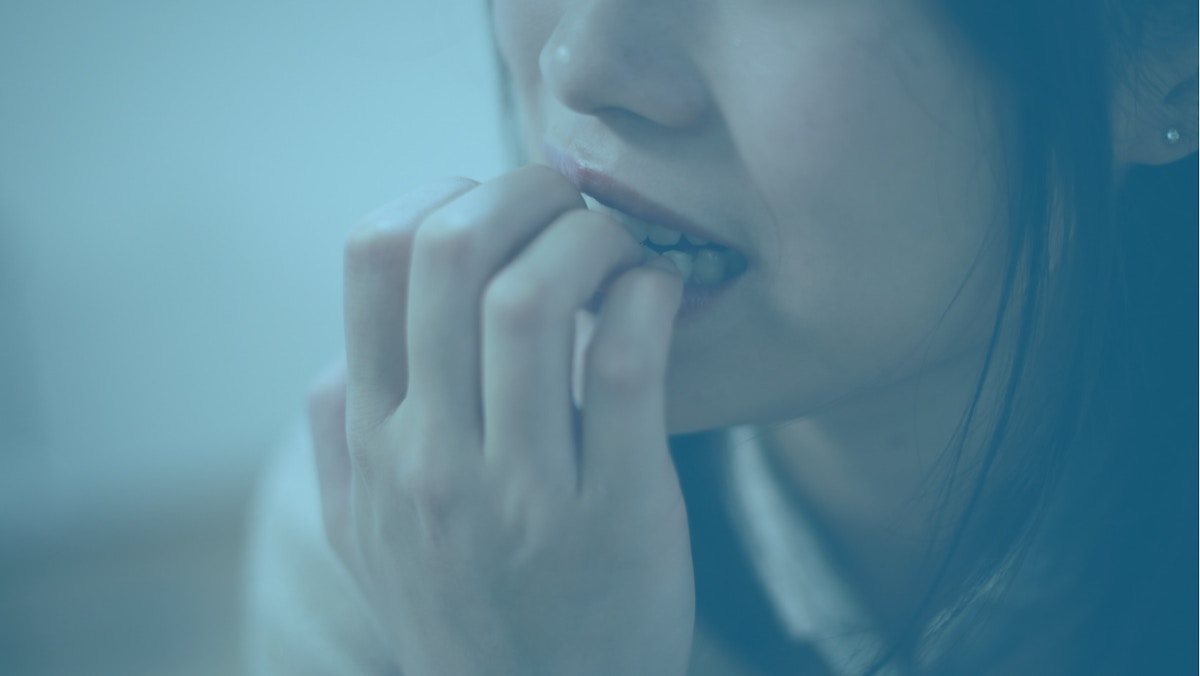

Nail Biting Disorder: Causes, Effects, and Treatment
Last Updated: Tue, January 23, 2024Nail biting usually begins in infancy and progresses throughout adulthood. While nail biting is a widespread issue, it can be triggered by a variety of factors ranging from stress to worry. It can also develop to a nail biting disorder with harmful effects.
Although it may appear that stopping the activity is easy, many people who have tried have failed. One of the main reasons? They didn’t address the root cause of their nail biting disorder.
In this post, we will talk about nail biting disorder, its causes, effects, and treatment.
What Is Nail Biting Disorder?
Nail biting can be a short, non-harmful, cosmetic problem.
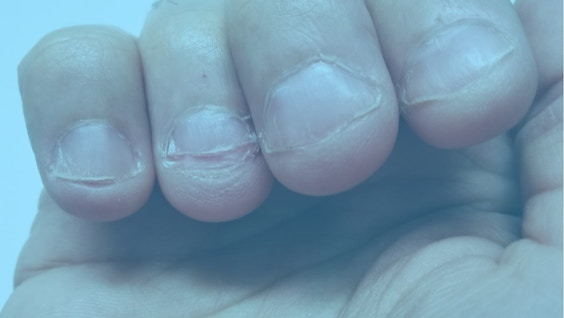
However, it can grow into a severe, long-term problem. Also known as onychophagia or onychophagy, nail biting disorder is a harmful problem characterized by prolonged, apparently uncontrollable nail biting.
The disorder causes damage not only to one’s fingernails, but also the surrounding tissue.
Causes of Nail Biting Disorder
Here are the causes of nail biting disorder:
1. Stress and Anxiety
A nail biting disorder can start due to stress and anxiety.
Unlike reactions like a racing heart or hyperventilation, which can result in the fight-or-flight response, nail biting is a strategy to relieve stress and anxiety. It’s because biting your nails feels pleasant.
2. Boredom
Boredom is another primary cause of nail biting disorder.
Since boredom stimulates the need to do something rather than nothing, some people bite their nails to cure boredom.
3. Mental Health Disorders
According to the fifth edition of the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, nail biting is a body-focused repetitive behavior disorder classified as an obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The American Psychiatric Association defines obsessive-compulsive disorder as unwanted thoughts, ideas, or feelings that drive individuals to perform something repetitively (compulsions).
This sort of behavior might disrupt a person's daily tasks and personal interactions. Not acting on compulsive behavior brings more misery than relief. It feels nice and relieves tension. In this case, it’s obsessive nail biting.
4. Genetics
If you bite your nails, you most likely picked up the practice from your parents. You picked it up not just via observation, but through heredity as well.
If the nail biter has obsessive-compulsive disorder, studies reveal that the condition likely runs in the family as well.
Effects of Nail Biting Disorder
Here are the effects of nail been disorder:
1. A lot of germs go under your fingernails.
Even if you wash your hands often, it is difficult to remove all of the bacteria and debris from between your nails.
So picture what you're exposing your body to by allowing bacteria and dirt to access your mouth.
When microorganisms from under your fingernails enter your body through nail biting, your chances of getting sick skyrocket.
2. Nail biting increases your risk of infection.
Biting your nails raises your chances of getting a nail infection. If the infection is bacterial, pus-filled blisters may form at the location.
The infection can also give way to other sickness such as fever.
3. It’s bad for your teeth.
Apart from eating, you must not use your teeth to bite anything.
Biting your nails on a regular basis might cause your teeth to move out of position. As a result, you might need corrective braces or a retainer.
Nail biting can also cause your teeth to crack or damage the enamel of your teeth. Your gums might also get infected or irritated as a result of the germs that enter your mouth as you bite your nails.
Additionally, bacteria on your fingers or nails can stay in your mouth, leading to foul breath.
4. You may get more hangnails or ingrown nails.
If you repeatedly bite at your nails, you're likely to bite off more than you planned.
When a piece of ripped flesh emerges at the root of your nail, you have a hangnail. Hangnails are exposed wounds that are readily infected. The best approach to avoid unpleasant sores is to prevent hangnails from growing in the first place by routinely moisturizing and not gnawing on your fingers.
Chewing your nails can also cause ingrown nails to grow beneath your fingers. Ingrown nails can cause discomfort and swelling. They can cause infection as well.
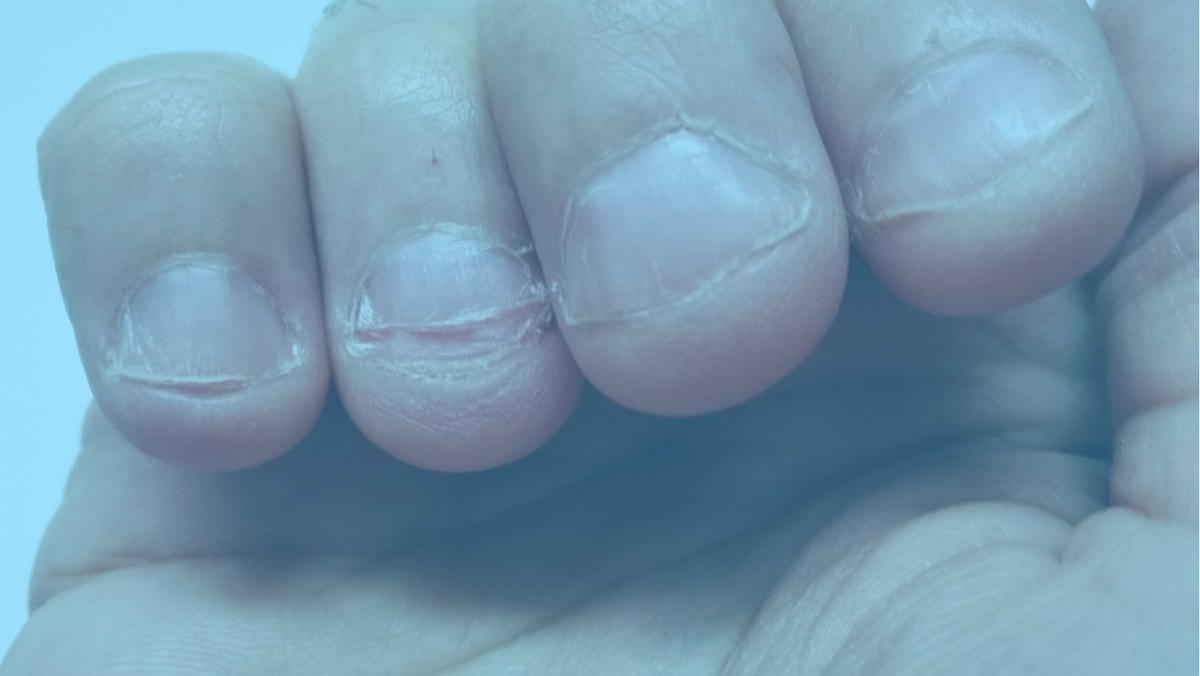
Treatments for Nail Biting Disorder
Here are the treatments for nail biting disorder:
Stress Management
Learning the triggers that make you uncomfortable, stressed, or bored is one way to quit nail biting.
If you cannot quit and your nail biting becomes excessive, consult your healthcare physician for a referral to a therapist.
Behavioral Therapy
If you have a severe nail biting disorder, cognitive behavioral therapy can help. In particular, it will help detect and change your behavior through therapy.
If your nail biting disorder is linked to a mental health issue, you may need medicine to be treated properly.
Conclusion
Nail biting is normal. However, it can develop into a nail biting disorder.
To treat it, you need to manage your stress levels. But you feel your behavior is out of control, you may need to explore behavioral therapy to figure out what is prompting the nail biting.
Building the right support system and using a sobriety app like I Am Sober can also help.
I Am Sober is a free app that helps you get some control back in your life.